Safety training is an important part of any business. Not just for those going into confined spaces or other hazardous atmospheres, but for those going into a formal office, a hospital, or anything in between. Safety training is a phrase often used to describe the training materials designed to teach occupational safety and health standards developed by various safety governing entities such as OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration), ANSI (American National Standards Institute), EPA (Environmental Protection Agency), or DOL (Department of Labor). Employers in the United States have a legal responsibility to educate employees on all workplace safety standards and the hazards their employees may face while working on the job. Proper safety training, whether through the employer or a third-party contractor, meets this requirement.
What are the benefits of safety training? Well, appropriate safety training can be linked to a reduction in the following:
- the number of injuries and deaths
- property damage
- legal liability
- illnesses
- workers' compensation claims
- missed work
For safety training to be successful, participants must be able to demonstrate knowledge of the standard and how it applies to their specific job. If presented correctly by a qualified trainer, it can promote a strong culture of safety in the workplace, one where veteran employees follow proper safety rules & guidelines and assist in promoting the same for new hires. This is achieved by both good, safety-conscious employees and solid trainers who keep employees engaged and keep their training program relevant and not too generalized.
But what happens when you neglect safety training at your workplace? In addition to a potential increase of the things listed above, here are a few times employers have felt the sting in their financial bottom line as well. Below, I have itemized OSHA citations reported in Jun-Aug 2015 for infractions of neglecting safety training for their employees. It's much cheaper to hire someone to do your training if you are unable to handle it yourself than to wait until OSHA hits you with related fines.
Company: Bigston Corporation
Inspection Site: Elk Grove Village, IL
Date of Findings: March 5, 2015
Type of Violation: Serious
29 CFR 1910. 134(k)(1): The employer did not provide respirator training that would ensure each employee could demonstrate knowledge of items in section (i)-(vii).
Penalty: $4,200.00
Source
Company: Grimco Inc.
Inspection Site: Akron, OH
Date of Findings: June 3, 2015

Type of Violation: Serious
29 CFR 1910.147(c)(7)(i): The employer did not provide training to ensure that the purpose and function of the energy control program are understood by employees and that the knowledge and skills required for the safe application, usage, and removal of the energy controls are acquired by employees.
Penalty: $7,000.00
Source
Company: Wilbert, Inc.
Inspection Site: Bellevue, OH
Date of Findings: February 2, 2015
Type of Violation: Serious
29 CFR 1910.174(c)(7)(i): The employer did not provide adequate training to ensure that the purpose and function of the energy control program was understood by employees.
Penalty: $7,000.00
Source
Company: D.R. Diedrich & Co.
Inspection Site: Milwaukee, WI
Date of Findings: February 2015
Type of Violation: Serious
29 CFR 1910.174(c)(7)(i)(A): Authorized employee(s) did not receive training in the recognition of applicable hazardous energy sources, the type and magnitude of the energy available in the workplace, and the methods and means necessary for energy isolation.
Penalty: $6,300.00
Source
Company: Ansley Metal Fabrication and Repair
Inspection Site: Donalsonville, GA
Date of Findings: March 26, 2015
Type of Violation: Serious
29 CFR 1926.761(b): The employer did not train each employee exposed to a fall hazard in accordance with the requirements of 29 CFR 1926.761.
Penalty: $4,900.00
Source
Company: New Homes Construction, Inc.
Inspection Site: Medford, NJ
Date of Findings: February 12, 2015
Type of Violation: Serious
29 CFR 1926.503(a)(2): The employer did not assure that each employee exposed to fall hazards was trained by a competent person qualified in the areas specified in 29 CFR 1926.503(a)(2)(i) through (viii).
Penalty: $3,080.00
Type of Violation: Serious
29 CFR 1926.1060(a): The employer did not provide a training program for each employee using ladders and stairways, as necessary, which would train each employee in the procedures to be followed to minimize hazards related to ladders and stairways.
Penalty: $3,080.00
Source
Company: Elite Storage Solutions, LLC
Inspection Site: Monroe, GA
Date of Findings: January 28, 2015
Type of Violation: Serious
29 CFR 1910.147(c)(7)(i): The employer did not provide training to ensure that the purpose and function of the energy control program are understood by employees and that the knowledge and skills required for the safe application, usage, and removal of the energy controls are acquired by employees.
Penalty: $7,000.00
Type of Violation: Serious
29 CFR 1910.157(g)(l): An educational program was not provided for all employees to familiarize them with the general principles of fire extinguisher use and the hazards involved with incipient stage fire fighting. The employer expected employees to use extinguishers to use extinguishers to fight incipient level fires, but did not implement a training program for the use of fire extinguishers.
Penalty: $5,500.00
Source
As you can see, the above fine amounts aren't generally high enough amounts to warrant closing up your company's doors, but they will certainly impact your profitability. Even more important is the realization that after paying the fine, you still have to pay for the training as well. Which can effectively double the initial cost if you were to train your employees in the first place. That number wouldn't even have taken into consideration the potential increase of compensation claims, property damage, missed work, injuries, legal liabilities and everything else discussed earlier. Keep in mind too that OSHA has made it easy to anonymously tip them off to an unsafe workplace. One phone call or email can now much more easily give an inspector a reason to visit. You must always take employee complaints seriously. In the case of the last two sources, you can see that having two fines for training can add up. If you expect your employees to use the provided fire extinguishers, you must train them in proper usage and be sure to have someone designated to check them monthly. Last of note is the company that did not have a qualified person train their employees; be sure if you are training your employees yourself, or in-house, that you (or whomever is doing the safety training) is qualified to do so. You may decide it be best to hire an outside person or company to do your safety training, but again, be sure they are at a qualified level to conduct the training. If you have any questions about this subject, feel free to contact us here at Safety Training Services by clicking below!






 the lowest total since BLS began collecting this data more than 20 years ago.
the lowest total since BLS began collecting this data more than 20 years ago.

 Fireworks themselves are dated back to 7th century China, where they were invented and used in many festivities. Fast forward to mid-17th century; Europe was blown away by Chinese fireworks and the popularity would rise and they were used for celebration of many important events. Finally in the late 18th century, the early European settlers brought this love of fireworks to this country and used them as rally devices, political attractions, and of course to celebrate important events.
Fireworks themselves are dated back to 7th century China, where they were invented and used in many festivities. Fast forward to mid-17th century; Europe was blown away by Chinese fireworks and the popularity would rise and they were used for celebration of many important events. Finally in the late 18th century, the early European settlers brought this love of fireworks to this country and used them as rally devices, political attractions, and of course to celebrate important events.
 Keep any type of ladder or pole (used to set up or light fireworks) at least 10 feet from any power lines.
Keep any type of ladder or pole (used to set up or light fireworks) at least 10 feet from any power lines. increase awareness of key safety issues. The idea is to decrease the number of unintentional injuries and deaths. NSC is also aligned with government agencies, such as OSHA, to help strengthen the influence of compliance in workplace safety.
increase awareness of key safety issues. The idea is to decrease the number of unintentional injuries and deaths. NSC is also aligned with government agencies, such as OSHA, to help strengthen the influence of compliance in workplace safety. Keep your meds in a secure place. Leaving them out in plain view can lead to theft.
Keep your meds in a secure place. Leaving them out in plain view can lead to theft. Clean all spills immediately
Clean all spills immediately Schedule calls for times when you will not be driving.
Schedule calls for times when you will not be driving.
 Possesses a concern for the welfare of others so trainers can serve as a safety advocate.
Possesses a concern for the welfare of others so trainers can serve as a safety advocate. It is the dealer’s responsibility to assist its customers in identifying training resources in order to satisfy its operator training obligations. Some dealers may provide training for their customers; others may choose to offer other training resources such as recommending a training company or getting the customer information on the manufacturer. Potential training resources are any entity offering instruction by a qualified instructor following an appropriate training program. This may be the manufacturer, rental company, independent training company or internal resources of the employer who rented the equipment.
It is the dealer’s responsibility to assist its customers in identifying training resources in order to satisfy its operator training obligations. Some dealers may provide training for their customers; others may choose to offer other training resources such as recommending a training company or getting the customer information on the manufacturer. Potential training resources are any entity offering instruction by a qualified instructor following an appropriate training program. This may be the manufacturer, rental company, independent training company or internal resources of the employer who rented the equipment. 
 The documentation (for verification) of training/familiarization should include the following information and should be retained for a period of four years as required by the ANSI/SIA A92 Standards:
The documentation (for verification) of training/familiarization should include the following information and should be retained for a period of four years as required by the ANSI/SIA A92 Standards:
 The Occupational Safety & Health Administration (OSHA), a government agency that issues and enforces regulations for employers to ensure workplace health and safety. These regulations are often referred to as standards, but they are in fact laws and compliance is mandatory.
The Occupational Safety & Health Administration (OSHA), a government agency that issues and enforces regulations for employers to ensure workplace health and safety. These regulations are often referred to as standards, but they are in fact laws and compliance is mandatory. Despite ANSI standards being voluntary, it is in every company’s best interest to comply. Because OSHA law many times is adopted from ANSI standards, the standards in the ANSI handbook are considered a consensus of what’s best to keep employees safe and because of this OSHA can decide that the company is not “free from recognized hazards” and cite the company for the “general duty” clause for not following ANSI standards. So as it turns out, ANSI standards may not be as “voluntary” as expressed. Keep yourself and your employee’s safe, by following the ANSI guidebooks as mandatory as OSHA law.
Despite ANSI standards being voluntary, it is in every company’s best interest to comply. Because OSHA law many times is adopted from ANSI standards, the standards in the ANSI handbook are considered a consensus of what’s best to keep employees safe and because of this OSHA can decide that the company is not “free from recognized hazards” and cite the company for the “general duty” clause for not following ANSI standards. So as it turns out, ANSI standards may not be as “voluntary” as expressed. Keep yourself and your employee’s safe, by following the ANSI guidebooks as mandatory as OSHA law.
 When properly trained, an operator is ready to operate any like-type of AWP as long as they are familiarized with the controls/safety devices of the other like-type equipment. Remember, when training takes place on a particular model of equipment, you must become “familiar” with other equipment models that were not included in the initial instruction so as not to put the operator at risk of danger/injury because of failure to know specific controls/safety devices. For example, certain manufacturers/models have different emergency lowering procedures, so familiarization is just as critical as general training. You wouldn’t want to be stuck up 30 ft in the air on a scissor lift with no one around, not knowing how to get down!
When properly trained, an operator is ready to operate any like-type of AWP as long as they are familiarized with the controls/safety devices of the other like-type equipment. Remember, when training takes place on a particular model of equipment, you must become “familiar” with other equipment models that were not included in the initial instruction so as not to put the operator at risk of danger/injury because of failure to know specific controls/safety devices. For example, certain manufacturers/models have different emergency lowering procedures, so familiarization is just as critical as general training. You wouldn’t want to be stuck up 30 ft in the air on a scissor lift with no one around, not knowing how to get down!
 Remember, familiarization must be facilitated by a qualified person. Only someone who is already trained and qualified may self-familiarize by reading and understanding the manual/operating instructions. Always refer to the operator’s manual if you have any questions, you might be surprised to find out how much information is actually in there!
Remember, familiarization must be facilitated by a qualified person. Only someone who is already trained and qualified may self-familiarize by reading and understanding the manual/operating instructions. Always refer to the operator’s manual if you have any questions, you might be surprised to find out how much information is actually in there!
 AWP equipment is very useful. It allows users access to usually inaccessible areas, usually at height. They can be used by maintenance workers, construction workers, firefighters (for emergency access); all while being operated by a single person (most models). AWPs can not only be used for transportation and/or access to certain areas, but also can be equipped with electrical outlets, compressed air (for power tools), and other specialist equipment.
AWP equipment is very useful. It allows users access to usually inaccessible areas, usually at height. They can be used by maintenance workers, construction workers, firefighters (for emergency access); all while being operated by a single person (most models). AWPs can not only be used for transportation and/or access to certain areas, but also can be equipped with electrical outlets, compressed air (for power tools), and other specialist equipment. In next week’s blog article, we will address many of these issues and shed light upon how to be ‘appropriately’ trained to use an AWP. This should serve as a thought-provoking piece until then, when we will discuss training, being ‘qualified’ and the importance of familiarization for the operator.
In next week’s blog article, we will address many of these issues and shed light upon how to be ‘appropriately’ trained to use an AWP. This should serve as a thought-provoking piece until then, when we will discuss training, being ‘qualified’ and the importance of familiarization for the operator. the safe use of the equipment.
the safe use of the equipment.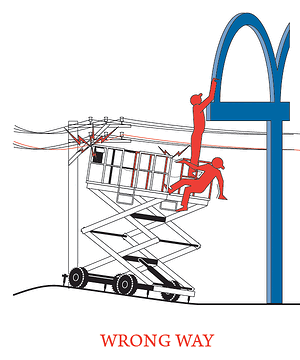 Maintain a minimum clearance of at least 10 feet, or 3 meters, away from the nearest energized overhead lines.
Maintain a minimum clearance of at least 10 feet, or 3 meters, away from the nearest energized overhead lines. Training is administered by professional safety trainers, specialized in delivering operator training for aerial equipment with an engaging course that exposes participants to multi-media content, cause & effect accident videos and current events. We also provide on-site training at your location, alleviating the need for participant travel.
Training is administered by professional safety trainers, specialized in delivering operator training for aerial equipment with an engaging course that exposes participants to multi-media content, cause & effect accident videos and current events. We also provide on-site training at your location, alleviating the need for participant travel.

