The history of the modern steel industry began in the late 1850s...
...and has really been going through major changes since 1970. It has often been considered to be an indicator of a country's economic progress, due to steel's critical role in infrastructural and overall economic development.
There has been a massive increase in the demand for steel since the turn of the millennium due to the economic boom of both China and India. World steel demand increased during the early 2000's; at the same time, many Indian and Chinese steel companies have risen to notability. Although China, as a whole, is both the the largest steel producer and consumer, ArcelorMittal is, in fact, the world's largest steel producing company.
The world steel industry peaked in 2007, when the steel-using sectors plunged and the construction industry used 50% of steel produced (the next highest usage was mechanical machinery & metal products with about 15% each). Although it deserves to be said that the slowdown was occurring already before the worldwide great recession that started in 2008. Demand was weak in 3 of the 4 major steel countries (NA, JP, EU) and steel mills strongly reduced output. Heavy cutbacks in construction caused falling prices (down about 40%) due to a sharply lowered demand.
 The industry witnessed a turnaround in late 2009 and continued to grow together with the global economic recovery. World crude steel production went up from 851 megatons (Mt) in 2001 to 1,548 Mt in 2012. This outperformed 2011 by almost 1.5%. Specifically, the U.S. steel sector will be dealing with excess capacity as its most significant issue due to the continued growth in new steelmaking facilities. However, on a good note, global steel demand is expected to improve gradually this year in comparison to 2012. In the United States, growth will be supported by attempts to sustain the economy's momentum, an improving labor market, strong momentum in the auto sector and recovery in construction markets. Increased demand should lead to improved profitability for 2014 and 2015, driven by better utilization rates. European steel demand is likely to fall further this year before a mild rebound takes hold in 2014. The big challenge for steelmakers in 2013 is to be cost competitive while maintaining enterprise value.
The industry witnessed a turnaround in late 2009 and continued to grow together with the global economic recovery. World crude steel production went up from 851 megatons (Mt) in 2001 to 1,548 Mt in 2012. This outperformed 2011 by almost 1.5%. Specifically, the U.S. steel sector will be dealing with excess capacity as its most significant issue due to the continued growth in new steelmaking facilities. However, on a good note, global steel demand is expected to improve gradually this year in comparison to 2012. In the United States, growth will be supported by attempts to sustain the economy's momentum, an improving labor market, strong momentum in the auto sector and recovery in construction markets. Increased demand should lead to improved profitability for 2014 and 2015, driven by better utilization rates. European steel demand is likely to fall further this year before a mild rebound takes hold in 2014. The big challenge for steelmakers in 2013 is to be cost competitive while maintaining enterprise value.
“The steel market in 2013 is off to a slow start, but signs of strength in some of the most important steel consuming market such as autos and energy (with a large inventory overhang at this point), provide some reason for optimism as we move into the usually seasonally stronger second quarter.”
--David Phelps, president of the American Institute for International Steel
Safety and Health in the Iron and Steel Industry
The original code of practice on safety and health in the iron and steel industry was adopted in 1981.
The International Labour Organization (ILO), founded in 1919, became the first specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) in 1946. The main aims of the ILO are to promote rights at work, encourage decent employment opportunities, enhance social protection and strengthen dialogue on work-related issues. The newest version of this code, updated 2005, reflects the many changes in the industry, its workforce, the roles of the competent authorities, employers, workers and their organizations, and on the development of new International Labour Organization instruments on occupational safety and health, focuses on the production of iron and steel and basic iron and steel products.

According to Part II, Section 5.1 of the Safety and Health in the Iron and Steel Industry Code, the choice and the implementation of specific measures for preventing workplace injury and ill health in the workforce of the iron and steel industry depend on the recognition of the principal hazards, and the anticipated injuries and diseases, ill health and incidents. Below are the most common causes of injury and illness in the iron and steel industry:
(i) slips, trips and falls on the same level;
(ii) falls from height;
(iii) unguarded machinery;
(iv) falling objects;
(v) engulfment;
(vi) working in confined spaces;
(vii) moving machinery, on-site transport, forklifts and cranes;
(viii) exposure to controlled and uncontrolled energy sources;
(ix) exposure to asbestos;
(x) exposure to mineral wools and fibres;
(xi) inhalable agents (gases, vapours, dusts and fumes);
(xii) skin contact with chemicals (irritants (acids, alkalis), solvents and sensitizers);
(xiii) contact with hot metal;
(xiv) fire and explosion;
(xv) extreme temperatures;
(xvi) radiation (non-ionizing, ionizing);
(xvii) noise and vibration;
(xviii) electrical burns and electric shock;
(xix) manual handling and repetitive work;
(xx) exposure to pathogens (e.g. legionella);
(xxi) failures due to automation;
(xxii) ergonomics;
(xxiii) lack of OSH training;
(xxiv) poor work organization;
(xxv) inadequate accident prevention and inspection;
(xxvi) inadequate emergency first-aid and rescue facilities;
(xxvii) lack of medical facilities and social protection.

As you can see quite well, the importance of safety and safety training in the steel and iron industry. With hazards ranging from noise to physical to chemical to ergonomics, it is a inherently dangerous industry to work in. Specific PPE should include, but not be limited to:
(a) molten metal resistant jackets and trousers;
(b) face shields or vented goggles;
(c) molten metal resistant gloves;
(d) safety footwear insulated against heat;
(e) respiratory protective equipment;
(f) protective helmets;
(g) hearing protection; and
(h) eye protection.
If you work in the industry, your next step should be to identify these issues at work. Have you found a problem in not knowing how to handle a situation listed above? Has any of these common injuries happened at your job? Is a problem in regards to training (or lack thereof)? Or retraining (annual refresher courses)? Unsatisfied with previous training/trainers? Safety Training Services, Inc. will train (and/or retrain) you and your employees on safety code compliance, confined spaces & other safety-related courses. Our site or yours, our hands-on courses will provide you with appropriate training to keep you safe and trained consistent to safety code requirements.
Maybe your issue is equipment or PPE? Whether you need new, used, rentals, servicing or just to figure out what equipment to use for a specific job, speaking to one of our professionals in our Technical division will help you find the right tool for the job in whatever capacity necessary.
Or simply contact our safety consulting division at (219) 554-2180 and found out how we will help identify problems and conduct a safety-related gap analysis for your company.




 Establish speed limits
Establish speed limits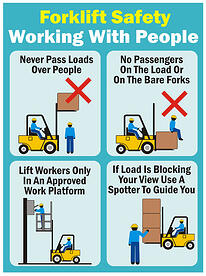


 Increase penalties for law-breakers
Increase penalties for law-breakers site
site
 The industry witnessed a turnaround in late 2009 and continued to grow together with the global economic recovery. World crude steel production went up from 851 megatons (Mt) in 2001 to 1,548 Mt in 2012. This outperformed 2011 by almost 1.5%. Specifically, the U.S. steel sector will be dealing with excess capacity as its most significant issue due to the continued growth in new steelmaking facilities
The industry witnessed a turnaround in late 2009 and continued to grow together with the global economic recovery. World crude steel production went up from 851 megatons (Mt) in 2001 to 1,548 Mt in 2012. This outperformed 2011 by almost 1.5%. Specifically, the U.S. steel sector will be dealing with excess capacity as its most significant issue due to the continued growth in new steelmaking facilities


 3 facts we, as workers, should be aware of.
3 facts we, as workers, should be aware of.





 The good news is that you can lower your blood pressure and cholesterol to reduce your risk of heart disease. Here are 4 ways you can do this (in no particular order):
The good news is that you can lower your blood pressure and cholesterol to reduce your risk of heart disease. Here are 4 ways you can do this (in no particular order):

 Treat every situation as potentially dangerous. OSHA's universal precautions require that all human blood or other potentially infectious materials be considered hazardous.
Treat every situation as potentially dangerous. OSHA's universal precautions require that all human blood or other potentially infectious materials be considered hazardous.