We're finally here! Welcome back to the 4th (and final) part of Safety Training Service's web series on general office safety! If you haven't had a chance to read parts 1 through 3, you may find them here:
Part One | Part Two | Part Three
According to OSHA, the majority of general industry accidents come in the form of slips, trips, and falls. These can result in back injuries, strains and sprains, contusions, and fractures.
OSHA also states that 15% of all accidental deaths are caused by slips, trips, and falls. In fact, they are second only to motor vehicles as a cause of fatalities. The standards for slips, trips, and falls are in the Code of Federal Regulations, under the heading "Subpart D" or 29 CFR 1910.22-30. This covers cause and prevention and included are housekeeping, ladder safety, floor openings and stairways.
 Slips can occur when floors or other working surfaces become slippery due to wet or oily processes, floor cleaning, leaks, or from materials and debris left in walkways.
Slips can occur when floors or other working surfaces become slippery due to wet or oily processes, floor cleaning, leaks, or from materials and debris left in walkways.
Trips can occur due to uneven floor or working surfaces, protruding nails and boards, from stretched carpet or bunched floor mats intended to prevent slipping, from holes or depressions in working surfaces, and from step-risers that are not uniform in height.
Falls can be a result of both slips and trips. In addition, improper ladder maintenance/use and stairways or elevated working surfaces that are not designed properly can result in a fall accident.
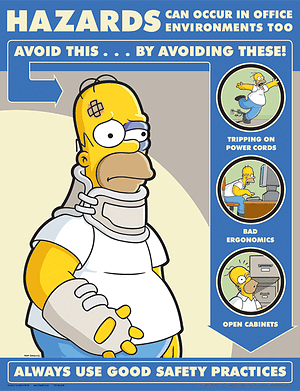
What can cause slips, trips, and falls? Just to name a few, ice, wet spots, grease, polished floors, loose flooring or carpeting, uneven walking surfaces, clutter, electrical cords, open desk drawers/filing cabinets, damaged ladder steps.
Here's a great compiled list of possible solutions for prevention. Some should be obvious, but ignored:
- Keep walkways and stairs clear of scrap and debris

- Coiling up extension cords, lines, and hoses when not in use
- Keeping electrical and other wires out of the way
- Wearing lug soles in icy weather
- Clearing parking lots, stairs, and walkways in snowy weather
- Using salt/sand as needed
- Where wet or potentially wet working conditions, maintain proper drainage and provide false floors, platforms, nonslip mats or floor surfaces, or other dry standing places (where practicable)
- Create nonslip surfaces in slippery areas by using no-skid waxes and/or grit-coated products
- Use slip-resistant footwear
- If a floor or working surface becomes wet, clean promptly and frequently
- Use/provide warning signs for wet floors
- Power/electrical cords that must cross walkways/aisles should be taped down (it is preferable to avoid this entirely by using floor plugs, if possible)
- Walkways/aisles should be kept clear at all times and should be wide enough for easy movement
- Carpet bulges or bunched up areas of carpet should be re-laid or stretched to prevent tripping
- Keep cabinets/drawers closed
- Eliminate clutter, obstructed work areas, and uneven floor surfaces
- Good lighting should be provided for all halls and stairwells, especially at night
- Stairs should have proper handrails and treads/risers should be maintained with slip-resistant surfaces, if possible
- Use handrails on stairs, don't run, and request help managing bulky loads. You must have an unobstructed view of the stairs
- Elevated storage and work surfaces should have guardrails, toe boards, and a permanent means of access
- Floor drains, pits, or any other floor opening should be covered or protected with guardrails
- Ladders should be properly maintained and have evenly spaced rungs and nonslip safety feet to reach items.
- Stools, chairs, boxes are NOT substitutes for ladders!
- Employees should be properly trained in the safe use of ladders
Ergonomics in the workplace
Having a comfortable work environment promotes a healthy physical and mental lifestyle. Adapting the workplace to you as a worker is the goal of an ergonomics program. But what really is "ergonomics?" It is a term often used and often misunderstood.
Ergonomics (according to Merriam-Webster's Dictionary) is "an applied science concerned with designing and arranging things people use so that the people and things interact most efficiently and safely." Ergonomics aims to improve the practicality, efficiency, and safety of a person working with a single machine or device (e.g., using a telephone, driving a car, or operating a computer terminal).
Setting up your workspace
You should set up your workspace into THREE zones:
- Primary Zone - This will be all the items you use on a very regular basis. This is the distance from your elbow to your hand. Such items may include your keyboard, mouse, and a notepad.
- Secondary Zone - These are the items within your arm's reach. Position the items that you use often but not as frequently as the ones in your primary zone. What do you use periodically? Maybe its your phone, calculator, and some trays for paperwork.
- Reference Zone - This is for your least-often used items. This zone is outside your arm's reach. Could be whatever you personally use least, it might be a utensil cup, plant(s), clock or even photos.
Ergonomics includes adjustments to your "body" as well. Listed below is 10 things to adjust, if necessary, to "you" in order to enhance your comfort at in your workplace.
- Take frequent recovery pauses from typing.

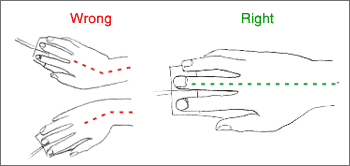
- Maintain a straight wrist position when typing.
- Avoid resting on your wrists while typing.
- Use a light touch on mouse and keys while typing.
- Maintain good health habits.
- Adjust keyboard and chair height to keep wrists straight.
- Place mouse next to the keyboard.
- Keep your feet on the floor or use a footrest for support.
- Support your lower back and use armrests, if possible, to comfortably support your arms.
- Throughout the day, adjust your chair positions, your posture and vary your tasks.
If you are using a laptop computer, optimizing its work surface, ergonomically speaking, can be a bit tricky. A special base that helps adjust the height and angle of a laptop monitor for a healthier and more comfortable work experience has been developed for exactly this situation.
Visual Discomfort
Research to date has not found any permanent effects on vision from computer use. However, eye strain and visual discomfort can result in reduced performance. In fact, it is the most common complaint among computer users.
So what do you DO about it? Its 2012, so chances are, computers are not going anywere anytime soon so here are some tips to help avoid eye strain at the computer:
- Blink more! We blink only 1/5th as much looking at a computer monitor as reading a newspaper. Try lowering your monitor so you are looking down, in order to help promote this.
- Move your monitor back a little bit. Our eyes are adapted for distance vision. Yet, most office work is done close to our eyes. Compensate for this by moving your chair periodically or adjust the distance/height of your monitor.
- Have a bigger monitor? Try increasing the size of your font/images. And of course, move back further from the screen.
- Try moving documents/items on your screen to different sides. Right eye dominant? Left eye? Try moving your email/documents to the left or the right and see if that is more comfortable for you.
- What about after all these tips, you still seem to have some discomfort? Try some glasses or seeing an eye care specialist. Seriously, its not the 70's/80's anymore, that stigma of the nerdy kid with glasses is gone! Get a sweet pair for the sole purpose of reading/working with computer monitors or similar devices. I am wearing mine as I type this, but use them generally just for this purpose and take them off when not working.
Regarding lighting of the work surface; it is suggested to have a ceiling light hung right above your computer monitor. This maximizes lighting of the overall work surface with minimal glare on the monitor itself. Not possible? Completely understandable. But lighting can have a considerable effect on both your comfort and performance. How? Oh, I'm so glad you asked. Let's take a look:
|
Fluorescent lights?
|
Harsh, excessively bright. Causes eye strains and glare.
|
|
Too little lighting?
|
Eye strain with paper documents, "gloomy" work atmosphere.
|
|
Windows?
|
Can cause lighting/glare problems, but given the choice most people would probably prefer having natural light and a view.
|
|
Direct Sunlight?
|
Not adjustable, unfortunately. Can be much brighter then what is actually needed.
|
Improving lighting has many benefits. It can reduce glare, increase work productivity and quality, and save on energy! Lighting should be lower then that for reading (many due to the computer monitor giving off its own light). The best way to optimize light levels should be to set a low level overall (overhead/indirect lighting), and use task lighting for situational use (desk lamps, undercabinet lights, etc.).
Two things I would like to mention, but won't spend as much time on is temperature/humidity and noise.
Its pretty simple actually, too high of a temperature cause fatigue and uncomfortablity which leads to slumping & slouching. Awkward postures are too be avoided, as they are bad for your health. Too cold of a temperature can lead to muscle tension, increased risk for tendinitis, and other such health risks/issues. Humidity also falls into this discussion, seeing as too low a level can cause dry skin and reduced snsation in your fingertips (increasing the amount of force necessary for various tasks). Too much humidity can make your environment feel "stuffy" and the temperature seems higher than it actually is. Humidity also has an effect on actual or perceived indoor air quality.
Noise usually is not an issue as far as being damaging to our hearing in an office environment, but the fact that it can be darn distracting to some makes it potentially devastating to worker productivity and/or performance. I can go on and on (I probably will later in another blog specifically geared towards noise in the workplace) but will cut to the important stuff for right now--what to DO when a noise problem arises!
- Reduce or eliminate at the source whenever possible.

- Maintain equipment to prevent noisy malfunctions.
- Isolate or enclose equipment that generates noise even when it's in good repair.
- Have conference rooms available for meetings and conversations.
As far as just a neighbor who playing music too loud? Be polite and ask them to turn it down or use headphones (if possible).
Lifting

If lifting is included in an employee's tasks, then the employer is obligated to teach the employee the best way to lift. You may choose to have
safety training for your employees covering ergonomics and lifting limits. Ultimately employees should know how to properly lift, when to get help, and when to use mechanical means rather than manually lifting an object.
Well, I am here to help with 5 solid tips to lift by:
- Keep object close to the body, don't reach out for an object.
- Move slowly and purposefully, don't jerk or twist.
- Feet should be shoulder width apart.
- Lift with your legs, not your back!
- Keep the back in a neutral position, bending should be done at the hips and knees. Keep knees slightly bent, never locked straight.
Rest/Stretch/Exercise Breaks
Breaks are encouraged! They help workers with a few minutes of recovery from the mental and physical demands of their jobs. This doesn't mean I'm trying to telling you to be a slacker, but micro breaks (1-3 minutes every hour, or half hour even) has shown to reduce discomfort while improving productivity. Use this time to get something to drink, have a quick stretch or even do some light exercise.
Remember for more relevant safety information, be sure to subscribe to our STS Blog & 'LIKE' us on Facebook. Feel free to leave a comment below to let us know what you think, and remember if you have any questions/concerns about your or your company's safety, you can contact Safety Training Services, Inc. by clicking the button below!
 Why take one over another?
Why take one over another? version of the previous topics and also includes Materials Handling in the mandatory topics, but adds 6 or so additional topics to be covered. The construction industry courses include even more additional topics for individual selection. The mandatory topics are different as well, tailored to include more construction specific topics, the most important difference is that of “Focus Four Hazards” which include: Fall Protection, Electrical, Struck By, and Caught in/Between.
version of the previous topics and also includes Materials Handling in the mandatory topics, but adds 6 or so additional topics to be covered. The construction industry courses include even more additional topics for individual selection. The mandatory topics are different as well, tailored to include more construction specific topics, the most important difference is that of “Focus Four Hazards” which include: Fall Protection, Electrical, Struck By, and Caught in/Between. Are these classes required?
Are these classes required?




 Luckily, many of these incidents/injuries are
Luckily, many of these incidents/injuries are  In 2008, the EPA estimated that of the 250 million tons of waste generated in the U.S., approximately one-third, or 83 million tons, was recycled or composted.
In 2008, the EPA estimated that of the 250 million tons of waste generated in the U.S., approximately one-third, or 83 million tons, was recycled or composted. produce the battery’s power.
produce the battery’s power. 
 Standing on chairs – particularly
Standing on chairs – particularly 

 Anytime you see something unsafe, report it to your facilities management department or supervisor. Things you might want to point out include sightings of:
Anytime you see something unsafe, report it to your facilities management department or supervisor. Things you might want to point out include sightings of: An office environment is considered to be one of the safest work environments, therefore to ensure a safe work environment; each individual must employ common sense, know physical limitations, display an attentive attitude towards their surroundings, and become aware of applicable compliance codes.
An office environment is considered to be one of the safest work environments, therefore to ensure a safe work environment; each individual must employ common sense, know physical limitations, display an attentive attitude towards their surroundings, and become aware of applicable compliance codes.
 job. In ancient times, it was tying rocks or bones to sticks for use as a hammer or sharpened to make hunting easier. Essentially, they established that using crude items could be used to make life easier. Ergonomics is just that, an applied science (not just a buzzword for marketers!) of work. That is, it’s intended to maximize productivity of workers by reducing/eliminating fatigue or discomfort. The literal definition of ergonomics, as Dictionary.com states, is “the study of the relationship between workers and their environment.” Also known as “biotechnology,” and first coined by Wojciech Jastrzebowski in 1857.
job. In ancient times, it was tying rocks or bones to sticks for use as a hammer or sharpened to make hunting easier. Essentially, they established that using crude items could be used to make life easier. Ergonomics is just that, an applied science (not just a buzzword for marketers!) of work. That is, it’s intended to maximize productivity of workers by reducing/eliminating fatigue or discomfort. The literal definition of ergonomics, as Dictionary.com states, is “the study of the relationship between workers and their environment.” Also known as “biotechnology,” and first coined by Wojciech Jastrzebowski in 1857.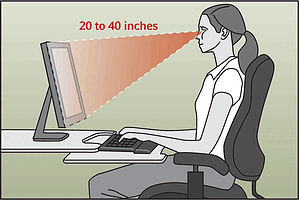

 mechanical compression, or sustained or awkward positions."
mechanical compression, or sustained or awkward positions."

 Slips can occur when floors or other working surfaces become slippery due to wet or oily processes, floor cleaning, leaks, or from materials and debris left in walkways.
Slips can occur when floors or other working surfaces become slippery due to wet or oily processes, floor cleaning, leaks, or from materials and debris left in walkways.


 If lifting is included in an employee's tasks, then the employer is obligated to teach the employee the best way to lift. You may choose to have
If lifting is included in an employee's tasks, then the employer is obligated to teach the employee the best way to lift. You may choose to have 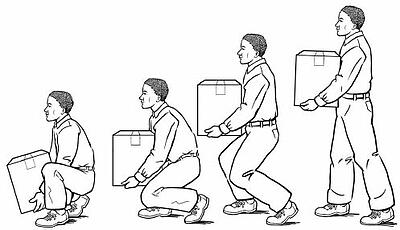

 PPE is designed to protect you from hazards related to your work.
PPE is designed to protect you from hazards related to your work.  Global Harmonization changed the label from MSDS to SDS, with a permanent change that came in 2015. OSHA requires that these data sheets be available to employees for potentially harmful substances handled in the workplace. Basically, these are intended to provide the workers and also emergency personnel the information necessary to safely handle/work with said substances. This information may include physical and/or chemical data and format may differ (currently there is no official way to format SDS). Below are some examples of what information you may find on SDS.
Global Harmonization changed the label from MSDS to SDS, with a permanent change that came in 2015. OSHA requires that these data sheets be available to employees for potentially harmful substances handled in the workplace. Basically, these are intended to provide the workers and also emergency personnel the information necessary to safely handle/work with said substances. This information may include physical and/or chemical data and format may differ (currently there is no official way to format SDS). Below are some examples of what information you may find on SDS.
 ALWAYS read/follow the labels on the ladder. Until the climber is familiar with this information, they are not considered "adequately" trained!
ALWAYS read/follow the labels on the ladder. Until the climber is familiar with this information, they are not considered "adequately" trained!